World leaders gathered in Baku, Azerbaijan, for the annual United Nations Climate Conference, COP29. This event brings together governments, businesses, and civil society representatives to promote concrete solutions to the global climate crisis.
Within this context, HINICIO and UNIDO presented a comprehensive market assessment focused on clean hydrogen in developing countries, as part of UNIDO’s Accelerate-to-Demonstrate Facility (A2D) initiative. The study analyzed key stakeholders and driving factors for clean hydrogen development, identifying challenges and opportunities in these economies.

Source: UNIDO, HINICIO – Market Assessment on Clean Hydrogen Innovation in Developing Countries – 2024
According to the Development Assistance Committee (DAC) list, there are currently 141 developing countries. The analysis revealed that clean hydrogen technologies are actively being implemented in 35 countries across five continents, with 114 projects in total. Of these, 41% focus on hydrogen production, 23% on mobility projects, 11% on ammonia production, and less than 5% on hydrogen technologies for the cement, iron, and steel industries.
By region, Latin America and the Caribbean host 36% of the projects, Asia 29%, and Africa 25%. In these three regions, most projects are primarily geared toward clean hydrogen production technologies.
Additionally, over 200 institutions, companies, and innovative organizations were identified in these countries, particularly in Asia, where nations like China and India lead in research and development initiatives, followed by countries in Latin America and the Caribbean such as Brazil, Costa Rica, and Colombia. However, while many projects are spearheaded by educational institutions, the industrial sector is reaching higher Technology Readiness Levels (TRLs), testing and adopting technologies at TRLs 6-9.
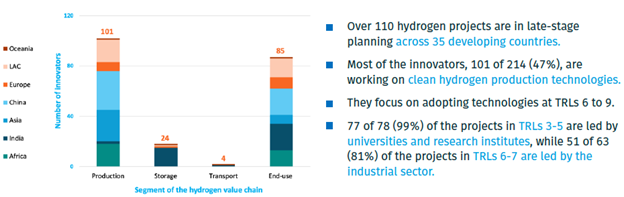
Source: UNIDO, HINICIO – Market Assessment on Clean Hydrogen Innovation in Developing Countries – 2024
Amid so many advancements and achievements, a key question arises: What are the main challenges innovators in these countries face in scaling their technologies and reaching higher levels of technological readiness?
The most notable challenges include:
- Financial support
- Lack of binding regulations
- Insufficient infrastructure
- Absence of off-takers
- Limited availability of advanced technologies
- Lack of skilled human resources
- Social and cultural resistance in some cases
By region, Latin America and the Caribbean host 36% of the projects, Asia 29%, and Africa 25%. In these three regions, most projects are primarily geared toward clean hydrogen production technologies.
On the other hand, at the national and regional levels, key strategies are being implemented to foster the development of a clean hydrogen industry. While progress is notable, significant challenges remain. In this context, what are developing countries doing to promote this industry and overcome the obstacles they face? At the regional level, what efforts are being made to strengthen the ecosystem and encourage integration among countries?
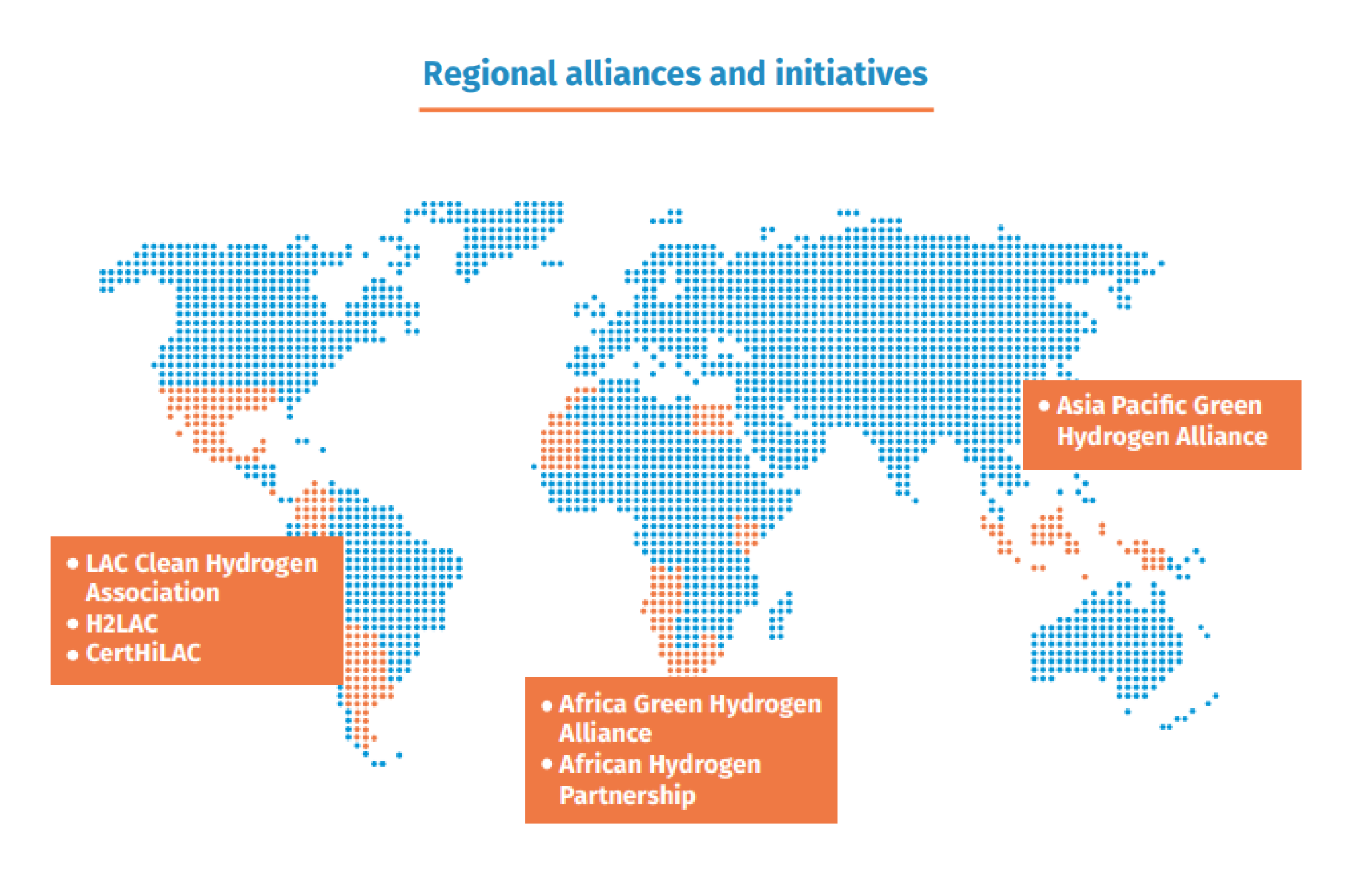
In the analyzed countries, national initiatives focus on public policies and regulatory development. Key steps include implementing certification systems in China and Brazil, as the CertHiLAC scheme in 12 Latin American countries.
Additionally, notable initiatives include the planning of hydrogen hubs in 15 countries and efforts to strengthen regulatory frameworks, with key examples in Brazil, Egypt, India, and Morocco.
Regional alliances and initiatives
Source: UNIDO, HINICIO – Market Assessment on Clean Hydrogen Innovation in Developing Countries – 2024
At the regional level, international cooperation has become a key pillar in developing the clean hydrogen market. Its initiatives often focus on prefeasibility studies, the design of regulatory frameworks, and technical and financial assistance. Countries such as Brazil, China, India, Morocco, and South Africa are currently receiving most of the support from international cooperation.
However, challenges persist in key areas such as insufficient infrastructure for exports, gaps in critical segments of the hydrogen value chain (particularly in transportation and storage), and limited coordination and technological exchange between countries.
Notable initiatives include the planning of hydrogen hubs in 15 countries and efforts to strengthen regulatory frameworks, with key examples in Brazil, Egypt, India, and Morocco.
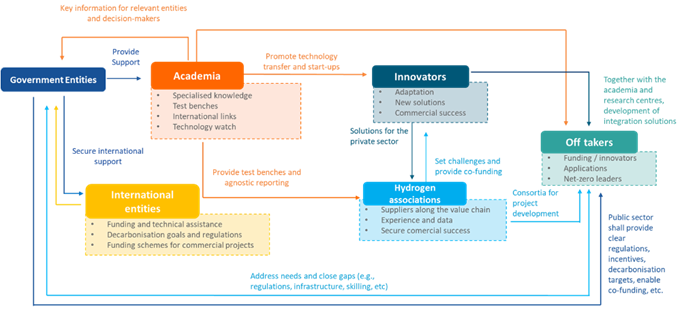
The presence of demonstration projects for innovative clean hydrogen solutions, a national roadmap, and a dedicated partnership for this resource are key factors in developing a competitive clean hydrogen ecosystem. However, only 47 of the 141 developing countries analyzed meet at least one of these criteria. By evaluating key aspects such as projects and innovation, financing mechanisms, hydrogen partnerships, roadmaps, and international collaborations, 16 countries were identified as leaders in clean hydrogen innovation within this group.

Source: UNIDO, HINICIO – Market Assessment on Clean Hydrogen Innovation in Developing Countries – 2024
Latin America and the Caribbean
With 41 demonstration projects, the region leverages its renewable-rich energy matrix, where more than 60% of energy comes from renewable sources. Opportunities include the export of hydrogen and ammonia, the promotion of sustainable mobility initiatives, and the strengthening of local clean ammonia production to reduce dependence on imports. Additionally, there is significant potential for exports to the United States and Europe, supported by projects targeting existing industries.
However, challenges include the lack of regulatory frameworks, limited technical expertise, and infrastructure difficulties in hydrogen and derivative production. Moreover, fostering acceptance from local communities remains a key challenge.
Asia
The hydrogen landscape in Asia includes 33 demonstration projects, highlighting significant potential for applications in clean hydrogen production, energy storage, and mobility. Projects in advanced planning stages, along with proximity to major consumers such as Japan, South Korea, and Singapore, position the region as a hub for growth.
However, regulatory diversity, varying levels of infrastructure development, and regional differences in access to technology both external and internal financing complicate projects. Additionally, a high dependence on fossil fuels exacerbates the challenges.
África
Africa has 28 demonstration projects, primarily focused on clean hydrogen production and mobility applications. Hydrogen-based microgrids represent a promising solution for providing clean energy to rural and remote communities, addressing the lack of access to electricity.
However, the region faces significant obstacles, such as a non-industrialized economy, a shortage of innovators, and gaps in technology and financial resources. The high dependence on fossil fuels, infrastructure challenges for hydrogen export, and political and economic instability further hinder development. With less than 25% of the population having access to energy, the urgency for transformative solutions is clear.
Key factors for the growth and consolidation of the clean hydrogen ecosystem in developing countries in the coming years:
Supporting the development of the hydrogen industry in developing countries is crucial for the growth of this market and for accelerating the global energy transition. To achieve this, it is essential to consider the following points:
- Private sector involvement is essential: Its participation drives investments, innovation, and the implementation of strategic projects.
- Public-private collaboration: Establishing strong partnerships between both sectors is crucial to addressing common challenges and seizing opportunities.
- Fostering an innovation ecosystem: Creating a conducive environment for research and development is vital to advancing clean hydrogen-related technologies and solutions.
- Constant adaptation and research: The ability to adapt to local needs and promote R&D programs is essential to overcoming technical and economic barriers.
- Focus on production and end-use applications: While most current projects focus on these areas, expanding efforts into other segments is necessary.
- Gaps in the value chain: Segments such as storage, transportation, and alternative vectors require more attention and development in developing countries.
- Strengthening regional cooperation: Collaboration between countries can facilitate the exchange of knowledge, resources, and best practices.
- Remaining challenges and obstacles: Despite significant progress, important barriers remain to be overcome to achieve a competitive and sustainable market.
For detailed information on the results of this study, we invite you to download the informational brochure here.
To access the full report on the official UNIDO and A2D Facility website, visit the following link: Market Assessment on Clean Hydrogen – A2D Facility (Full report).
Additionally, don’t miss the webinar “Accelerating Innovation in Clean Hydrogen – Market Assessment Launch,” where experts from Hinicio and UNIDO will share and discuss these key findings.
- When: Wednesday 27, November
- Time: 2:00 – 3:00 p.m. CET
Link to the registration: Clean Hydrogen Market Assessment Launch – Webinar Registration.







